| Function (not disease relevant) |
| Drug/chemo/stress |
Methods |
Sample/condition |
Expression pattern |
Dysfunction type |
Description |
PMID |
|
RNA immunoprecipitation, Immunoblotting and immunostaining of chromosomes, Fluorescent polarization assays, Electrophoretic mobility shift assays |
Drosophila, S2 cell lines |
|
interaction |
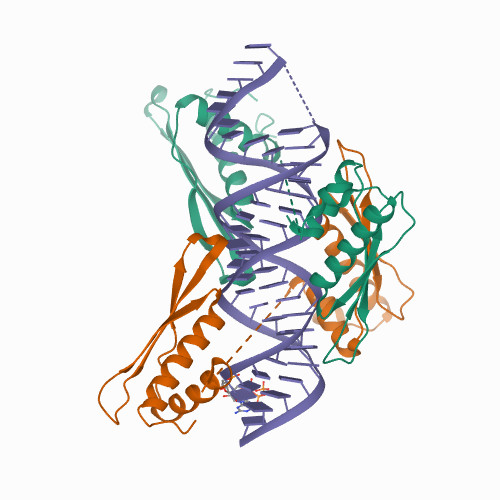
Our research provides structural insights into the interactions between MLE dsRBDs and R2H1 and facilitates a deeper understanding of the mechanism by which MLE tandem dsRBDs play an indispensable role in specific recognition of roX and the assembly of theMSL-DCC inDrosophila dosage compensation |
30649456 |
|
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
mutation |
Genetic rescue by roX orthologs and engineered synthetic lncRNAs showed that altering the number of focal, repetitive RNA structures determines roX ortholog function. Genomic occupancy maps of roX RNAs in four species revealed conserved targeting of X chromosome neighborhoods but rapid turnover of individual binding sites. Many new roX-binding sites evolved from DNA encoding a pre-existing RNA splicing signal, effectively linking dosage compensation to transcribed genes. Thus, dynamic change in lncRNAs and their genomic targets underlies conserved and essential lncRNA-genome interactions. |
26773003 |
|
loss-of-function, knockdown, |
|
down-regulated |
expression |
RNA-on-X 1 and 2 in Drosophila melanogaster fulfill separate functions in dosage compensation. |
30532158 |
|
Protein clonin, NMR |
Drosophila S2 cells |
|
|
dsRBD1 mutants in which dsRNA binding in vitro is strongly compromised do not affect roX2 RNA binding and MLE localization in cells |
30805612 |